Deep Understand How Does Payment Processing Work?
Payment processing is a crucial part of any e-commerce business. Without an efficient payment processing system, you cannot sell your products or services online. To process payments, merchants need to partner with a financial institution that specializes in e-commerce payment solutions, as well as other vendors such as a gateway processor and third-party software providers. In this blog post, we’ll cover the basics of how payment processing works and who is involved in the process. If you currently operate an e-commerce website or are thinking about launching one soon, it will help you understand the nuances associated with payment processing so that you can make informed decisions on how to move forward. Let’s get started!
How does payment processing work?
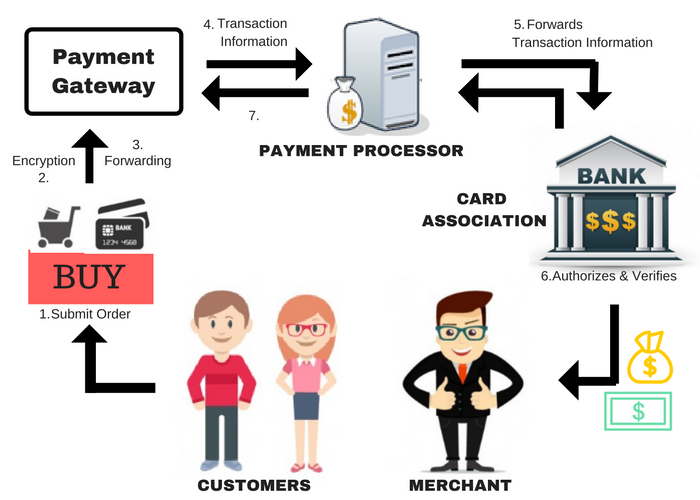
In order for both buyers and sellers to be protected when conducting online transactions, there are several steps that must occur during the payment processing flow. The parties involved in these steps include the customer, the merchant, a third-party payment processor, an authorized gateway, and the customer’s financial institution. When a customer initiates an online payment transaction, they are redirected to the merchant’s website. The merchant is responsible for hosting a secure website where customers can submit payment information during an online transaction. If a customer uses a credit or debit card to make a purchase, the card information is sent to a third-party payment processor where it is verified and verified again by the customer’s financial institution.
How does a merchant receive payment from a customer?
The flow of funds in the online payment processing chain goes from the customer to the merchant. The customer initiates the payment by submitting their payment information. The third-party payment processor, in this case, the acquiring bank of the merchant, receives payment for the goods or services ordered by the customer. The acquiring bank then sends the payment amount to the merchant’s account where the funds are deposited. The merchant then has several options for receiving the funds from their bank. They can choose to have the funds deposited directly into their bank account, have the funds deposited into a merchant account, or have the funds go directly into their money market fund account.
Who Processes Payments?
There are two scenarios in which a payment processor is involved in an online transaction. If a customer uses a credit or debit card to make a purchase, they are routed to the payment processor where they are verified and verified again. And if a customer wants to pay with cash, check, or an alternative payment method such as cryptocurrency, a payment processor is involved as well. The processor routes the transaction to the acquiring bank where it is verified against fraud detection rules. The acquiring bank then sends the payment amount to the payment processor where it is verified again against another set of fraud detection rules. If the transaction is verified, the payment processor routes the payment amount to the merchant’s account where the funds are deposited.
The main payment processing participants are listed below
An authorized participant is involved in the payment processing to complete an offline or online payment.
Cardholder
A person who receives a debit or credit card from an issuing bank and opens an account linked to it is known as a cardholder. They pay for items or services using the card or account.
Cardholder’s Bank
An issuing bank verifies that a client is eligible to become a credit or debit card holder. Furthermore, it verifies that the client is eligible to become a cardholder.
Merchant
A merchant is a person or company that sells products or services. If this individual or company sells those items online, they are referred to as an e-commerce merchant.
A merchant accepts payment cards and receives funds through a merchant account. An acquiring bank provides a merchant account to receive payment card transactions
An acquiring bank receives payment info from a merchant when a buyer pays for an item. The issuing bank forwards the payment info to the card holder’s bank via a card association network. If the payment info is accurate and there are sufficient funds in the buyer’s account, the issuer accepts the transfer of funds from the buyer’s account to the merchant’s account.
Using a digital wallet such as Google Pay, Apple Pay, or any similar payment method, the merchant submits transaction information to the wallet operator if the buyer pays for goods or services. The data are then sent to the payment processor, the acquiring bank, and other relevant parties.
Merchant’s Bank
A merchant’s bank is a financial institution through which a business organization opens a merchant account, and maintains it.
Payments via credit and debit cards are accepted by this bank and forwarded to the merchant’s account.
Payment Processor
A payment gateway processes card payments using a payment processor. It acts as a mediator between merchants, card networks, merchant banks, and other parties to complete card payments. PCI standards must be adhered to by every payment processor to ensure that payment processing procedures are compliant. PCI compliance includes adhering to operational and technical standards to protect and secure credit card information that cardholders submit for credit card payments.
Note: PCI compliance ensures that credit card information is safeguarded and protected by adhering to operational and technical standards in credit card payments.
Payment Gateway
When a customer makes a purchase, the purchaser’s credit card information is encrypted and sent to the payment processor via a payment gateway. An online connection is established between the purchaser’s bank and the seller’s bank using a payment gateway.
Card Associations
MasterCard, American Express, Discover, and Visa are card associations. They regulate qualification standards, interchange rates, and transaction terms for all payment processing participants.
They serve as mediators between issuing banks and merchant banks in case of disputes.
The Stages of Payment Processing
In addition to ensuring a high level of security during the transaction, payment processing stages guarantee that the payment is processed in a timely manner. These stages are implemented by payment processing companies in accordance with strict regulations
Authorization
Every party involved in a payment processing procedure is verified as being eligible to participate by authorization.
A process consists of the following stages:
- Step 1: When purchasing goods or services, the cardholder provides their credit card number to the merchant. Online payments are processed through payment gateways, whereas physical stores accept payment requests at point-of-sale terminals.
- Step 2: Merchants send payment requests to their set payment processors to obtain approval. If the customer pays for items or services through a digital wallet such as Google Pay, Apple Pay, or another similar method, the transaction information is sent to the wallet operator, who then forwards it to the payment processor.
- Step 3: The request for payment is delivered to the card association through the payment processor, with the issuing bank as the destination.
- Step 4: When an authorization request is received from a credit card company, the issuing bank receives the data elements, such as the card verification value (CVV), expiration date, and address verification services (AVS).
- Step 5: An issuing bank either declines or approves the transaction. The transaction may be declined for the following reasons: insufficient funds on the credit card, the payment date has passed, or the cardholder’s account is invalid or expired.
- Step 6: The card association, the merchant bank, and the merchant all receive notification of whether the purchase has been authorized or not when the issuing bank sends the approval or denial notification.
It takes just a few seconds or minutes to approve payments with advanced payment technologies.
Settlement and Funding
After the customer has paid for the goods or services, the merchant receives the payment during settlement. Settlement occurs when the following parties handle the funds and the payment processing:
- Step 1: The payment processor receives a batch of authorized payments from the merchant.
- Step 2: The payment processor forwards the transaction data to the card association.
- Step 3: The card association notifies the relevant issuing bank within their network of the requested debit.
- Step 4: The issuing bank debits the cardholder’s account with the requested amount for the payment.
- Step 5: The requested funds are then transferred to the merchant bank by the issuing bank. Interchange fees are paid at this stage.
- Step 6: The merchant bank credits the merchant account with the funds in question
Credit Card Interchange
Acquiring banks settle and clear payment data for their merchants, who finish approved credit card payments. In addition to costs and fees, this procedure refers to payments made by the acquiring bank to the issuing bank.
Third-party gateways
A gateway is a layer of software that connects a merchant’s website with a payment processor’s software. If the merchant uses a standalone solution that does not use a third-party gateway, they will have to integrate their technology with the payment processor. Third-party gateways, such as Authorize.net and PayPal, allow merchants to take advantage of established software to process payments. Gateways can also handle risk management, fraud detection, and end-to-end encryption. Some gateway providers have created their own proprietary software that provides more functionality than the standard gateway software, but at the expense of less flexibility when selecting payment processing software.
Third-party software providers
Third-party software providers are, as the name suggests, software providers that do not issue merchant accounts. Instead, they work with third-party payment processors to provide services such as reporting, fraud detection, and payment processing. These types of providers can be very beneficial to growing e-commerce businesses, especially because they don’t require the merchant to obtain a merchant account. However, they usually come with higher fees than merchant account-based payment processing.
Conclusion
In this article, we looked at how payment processing works and who is involved in the process. For an e-commerce business to receive funds for the goods or services sold to a customer, a merchant needs to have a merchant account with a financial institution that provides payment processing services. When a customer initiates an online payment transaction, they are redirected to the merchant’s website. The merchant is responsible for hosting a secure website where customers can submit payment information during an online transaction. The customer then has several options for payment, including credit or debit card, cash, or check. When the customer submits their payment information, the transaction is routed to the payment processor where it is verified again against fraud detection rules. If the transaction is verified, the payment processor routes the payment amount to the merchant’s account where the funds are deposited.